Transport networks worldwide are experiencing a fundamental transformation driven by automation technologies that are eliminating manual processes, enhancing precision, and fundamentally changing how transport operations function. From the moment a vehicle is dispatched until it reaches its destination, automation technologies now influence almost every operational decision and workflow. This technological shift represents not merely an efficiency improvement, but a profound reorganization of transport operations toward greater safety, consistency, and responsiveness.
The impact of automation extends across all transport modes road networks with intelligent traffic management, railways with autonomous yard operations, aviation facilities with automated aircraft servicing, and maritime ports with robotic cargo handling systems. Each sector is discovering that automation does not simply speed up existing processes; it enables entirely new operational approaches that were impossible with manual systems. Understanding these transformations provides insight into how transport networks are evolving to meet the demands of growing populations and increasing cargo volumes.
Automated Traffic Control and Congestion Management
Urban traffic congestion represents one of the most persistent challenges facing modern cities, consuming billions of hours annually in lost productivity and contributing significantly to emissions. Traditional traffic management relied on fixed signal timing or simple sensors that were slow to respond to changing conditions. Automated traffic control systems represent a quantum leap in sophistication and effectiveness.
Modern intelligent traffic control systems integrate real-time data from thousands of sensors distributed throughout road networks. Vehicle detection systems monitor traffic flow on every major road, intersection, and highway. This continuous data stream feeds into sophisticated algorithms that optimize signal timing not just for individual intersections, but for entire network corridors. The system dynamically adjusts green light duration, turning sequences, and even lane allocations based on actual traffic conditions. The result is measurable reductions in travel times, less congestion, fewer stops and starts that waste fuel, and improved safety through more predictable traffic patterns.
Adaptive signal control systems can detect incidents accidents, disabled vehicles, or unexpected congestion and automatically reroute traffic to parallel routes. Emergency vehicles trigger signal coordination that clears a path, enabling faster response times. These systems continuously learn from traffic patterns, identifying recurring congestion points and optimizing the overall network response. Cities implementing advanced automated traffic control have documented congestion reductions of 15-25%, fuel consumption decreases of 10-15%, and emissions reductions proportional to fuel savings.
Autonomous Yard Operations at Transport Hubs
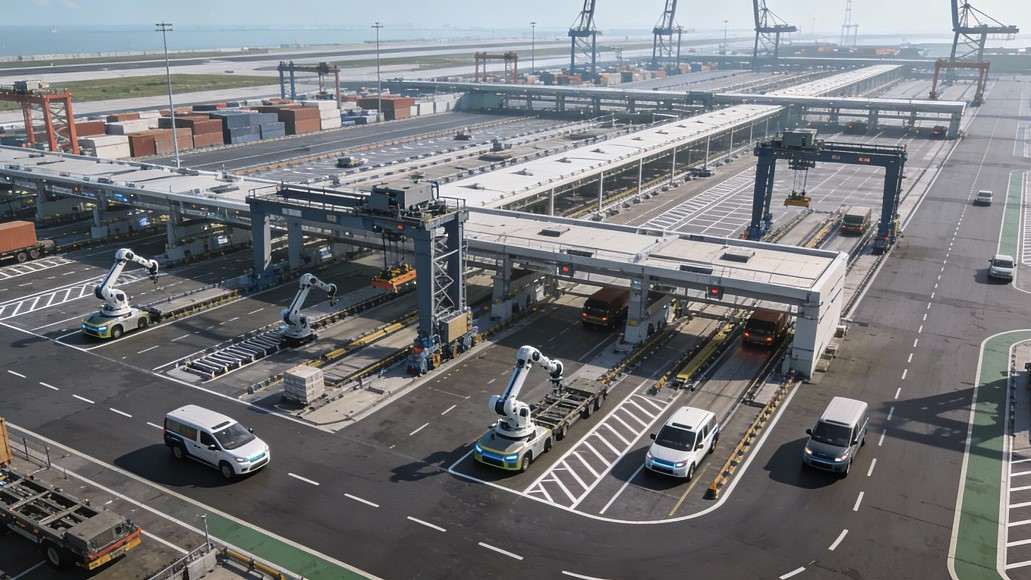
Ports and logistics terminals represent incredibly complex operational environments where vessels, trucks, trains, equipment, and cargo converge. Traditional yard operations relied on dispatchers coordinating dozens of equipment operators, each making real-time decisions about vehicle positioning, cargo loading sequences, and equipment allocation. This human-dependent system inevitably suffered from variability, inefficiency, and safety risks.
Autonomous yard operations represent a complete reimagining of how transport terminals function. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and autonomous trucks move cargo throughout the terminal based on real-time optimization algorithms. These vehicles communicate constantly with the terminal’s control system, which coordinates all movements to minimize conflicts, eliminate unnecessary positioning moves, and optimize loading sequences. Cranes and other terminal equipment operate based on automated dispatching instructions, knowing precisely which container to load, where to position it, and when the next action occurs.
The advantages extend beyond pure efficiency. Autonomous systems operate continuously without shift changes, fatigue-related errors, or safety incidents from operator mistakes. Cargo handling follows optimized sequences that minimize equipment wear and damage to goods. The ability to operate in harsh conditions extreme temperatures, high humidity, chemical-laden environments without affecting worker health becomes feasible. Ports implementing autonomous yard operations have documented vessel turnaround time improvements of 20-40%, equipment utilization increases of 30-50%, and dramatic reductions in safety incidents.
Robotics in Maintenance Facilities and Asset Inspection
Maintaining transport assets vehicles, tracks, infrastructure, equipment represents an enormous operational challenge given the scale of modern transport networks. Traditional maintenance relied on scheduled inspections where workers physically examined assets at predetermined intervals, often identifying problems only after failures occurred. This reactive approach resulted in expensive emergency repairs, unexpected downtime, and safety hazards.
Robotic systems are transforming maintenance operations in fundamental ways. Automated inspection robots equipped with high-resolution cameras, thermal imaging, ultrasonic sensors, and other diagnostic equipment conduct detailed inspections far faster than human workers could manage. These systems detect wear patterns, identify structural defects, locate cracks, and measure component degradation with precision impossible for manual inspection. The continuous data from automated inspections feeds predictive algorithms that forecast when components will fail, enabling maintenance to be scheduled well in advance.
Robotic maintenance systems also perform repetitive, physically demanding, or hazardous maintenance tasks. Automated rail grinding machines maintain track geometry at consistent standards. Robotic welding systems repair damaged components. Autonomous cleaning systems maintain equipment and facilities. These systems eliminate the physical strain that causes injury in maintenance workers, improve consistency and quality of work, and reduce the time equipment spends out of service. Facilities implementing robotic maintenance have documented maintenance cost reductions of 20-35%, equipment reliability improvements of 25-40%, and dramatic improvements in worker safety.
Intelligent Scheduling and Dynamic Optimization
Transport scheduling has always been challenging. Transport operators must coordinate complex operations with multiple constraints vehicle availability, crew shift requirements, maintenance schedules, demand fluctuations, regulatory requirements, and customer preferences. Traditional scheduling created fixed timetables weeks or months in advance. These static schedules often proved inefficient when actual demand differed from forecasts or unexpected disruptions occurred.
Intelligent scheduling systems employ advanced algorithms to dynamically optimize transport operations in response to real-time conditions. Train scheduling systems adjust departure times, platform assignments, and speed profiles based on passenger loads, track conditions, connecting service synchronization, and operational priorities. Truck dispatching systems assign loads to vehicles, determine routing, and adjust schedules based on live traffic data, weather conditions, and driver availability. Airline systems optimize aircraft utilization, crew scheduling, and flight sequencing based on demand forecasts, maintenance windows, and fuel efficiency considerations.
These intelligent systems continuously learn from operational data, identifying patterns that enable progressively better optimization. A scheduling algorithm learns which routes tend to experience delays and adjusts sequencing accordingly. It identifies periods of high demand and ensures adequate capacity. It optimizes crew assignments to minimize fatigue while maximizing efficiency. The results are schedules that adapt smoothly to changing conditions, minimize delays, optimize resource utilization, and improve customer satisfaction. Airlines and rail operators using dynamic scheduling have documented improvements in on-time performance, equipment utilization, and cost efficiency ranging from 5-15%.
Safety Enhancement Through Automated Vigilance
One of automation’s most significant benefits relates to safety. Automated systems operate with perfect consistency, do not experience fatigue or distraction, and follow procedures exactly as programmed. Automated monitoring systems continuously watch for safety hazards, detecting problems that tired human operators might miss.
Vehicle safety systems exemplify this principle. Automated braking systems detect imminent collisions and initiate braking faster than human reflexes. Lane-keeping systems prevent vehicles from drifting into adjacent lanes. Driver fatigue monitoring systems alert operators when vigilance declines. These systems have reduced accident rates in fleets implementing them by 30-50%. Similarly, automated platform screen doors at rapid transit systems have virtually eliminated falls onto tracks. Automated fire detection and suppression systems in vehicle maintenance facilities prevent small incidents from becoming catastrophic.
The Human-Automation Collaboration Model
Despite widespread automation, successful transport operations recognize that humans and automation systems must collaborate effectively. While automation excels at routine, repetitive tasks and handling normal conditions, human workers remain essential for handling exceptions, making strategic decisions, and addressing unexpected situations. The most successful implementations create clear roles where automation handles high-volume, routine operations while human workers focus on complex problem-solving, safety oversight, and strategic optimization.
Automation has actually increased demand for skilled workers capable of understanding these systems, interpreting their outputs, and making informed decisions based on automated recommendations. Maintenance technicians must understand robotic systems. Dispatchers must work effectively with intelligent scheduling algorithms. Traffic managers must interpret real-time traffic data and optimize network performance. This evolution means that transport operations are becoming increasingly knowledge-intensive, requiring workers with stronger technical skills and analytical capabilities.
Meeting the Challenges of Growth and Change
Global transport demand continues increasing year after year. Population growth, urbanization, and economic development create seemingly endless demand for transport services. Traditional approaches relying on proportionally increasing labor would face practical and economic limits. Automation provides the means to accommodate this growing demand while maintaining safety, improving efficiency, and controlling costs.
Moreover, transport networks must increasingly accommodate new technologies electric vehicles, autonomous vehicles, shared mobility services while maintaining compatibility with existing systems. Automation and flexible operational systems make this technological transition feasible. A network that automated its operations can integrate new vehicle types, accommodate new service models, and adapt to technological changes far more readily than one still dependent on traditional, manual processes.
The transformation of transport operations through automation represents one of the most significant shifts in infrastructure management in decades. By automating routine operations, optimizing scheduling and routing through intelligent algorithms, and employing robotics for maintenance and inspection, transport networks are becoming safer, more efficient, and more responsive to customer needs. This automation-driven transformation is enabling transport networks to meet the challenges of growth, technological change, and increasing complexity that characterize the modern world.